Exploring the future of health information technology and the predictions made by experts, this introduction sets the stage for an insightful discussion that delves into key trends, advancements, and challenges shaping the healthcare landscape.
Providing a comprehensive overview of the current state of health information technology and how technological innovations are revolutionizing healthcare practices.
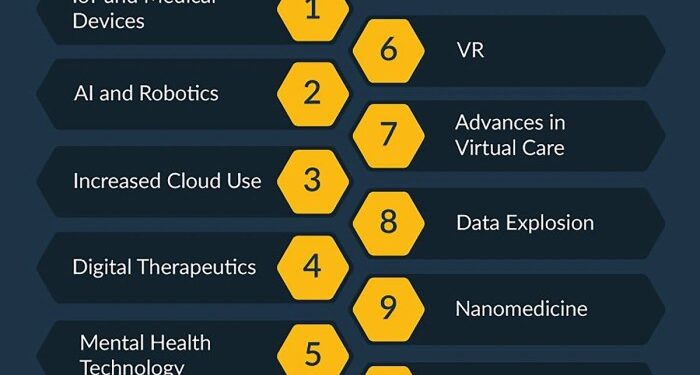
Overview of Health Information Technology Trends

Health information technology has become a crucial component of the healthcare industry, revolutionizing the way patient data is stored, accessed, and utilized. With the increasing digitization of medical records and the development of advanced technologies, the landscape of health information technology is constantly evolving.
Current Landscape of Health Information Technology
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs) have become standard practice in healthcare facilities, improving the efficiency and accuracy of patient data management.
- Telemedicine and remote patient monitoring have gained popularity, allowing patients to receive care from the comfort of their homes.
- Healthcare analytics and artificial intelligence are being used to analyze large datasets and make informed decisions for patient care.
Key Trends Shaping the Future of Health Information Technology
- Interoperability: Efforts are being made to improve the seamless sharing of patient data across different healthcare systems and providers.
- Personalized Medicine: Advances in technology are enabling the customization of treatment plans based on individual patient data and genetic information.
- Cybersecurity: With the increasing digitization of healthcare data, there is a growing focus on enhancing cybersecurity measures to protect patient information from cyber threats.
Advancements in Technology Influencing Healthcare Practices
Advancements in technology such as wearable devices, mobile health apps, and telehealth platforms are transforming healthcare practices by increasing access to care, improving patient outcomes, and enhancing the overall patient experience. These innovations are enabling healthcare providers to deliver more personalized and efficient care to patients, ultimately leading to better health outcomes.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence in Health Information Technology
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming the landscape of health information technology by revolutionizing how data is processed, analyzed, and utilized in healthcare systems. AI algorithms have the capability to interpret complex medical data at a rapid pace, leading to improved decision-making, personalized treatment plans, and enhanced patient outcomes.
AI Applications in Healthcare Data Management
AI is being utilized in various applications within healthcare data management, such as:
- Medical Imaging Analysis: AI algorithms can analyze medical images like X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans to detect abnormalities and assist radiologists in diagnosis.
- Predictive Analytics: AI can predict patient outcomes, identify high-risk individuals, and prevent potential health issues by analyzing large datasets and patterns.
- Natural Language Processing: AI-powered tools can extract valuable insights from unstructured data like physician notes, patient records, and research articles.
- Healthcare Chatbots: AI chatbots can provide personalized assistance, answer patient queries, and schedule appointments, improving patient engagement and satisfaction.
Benefits and Challenges of Integrating AI in Health Information Technology
- Benefits:
- Enhanced Efficiency: AI can automate repetitive tasks, streamline workflows, and reduce administrative burden on healthcare professionals.
- Improved Diagnostics: AI algorithms can assist in early disease detection, accurate diagnosis, and personalized treatment recommendations.
- Cost Savings: By optimizing resource utilization, reducing medical errors, and predicting healthcare trends, AI can lead to significant cost savings in the long run.
- Challenges:
- Data Privacy and Security: Integrating AI requires handling sensitive patient data, raising concerns about privacy, security, and compliance with regulations like HIPAA.
- Interoperability Issues: Ensuring seamless integration of AI systems with existing health IT infrastructure and interoperability across different platforms can be challenging.
- Ethical Considerations: AI algorithms must be transparent, accountable, and unbiased to avoid potential biases, errors, or discrimination in patient care.
Interoperability and Data Exchange in Health Information Systems
Interoperability in health information technology refers to the ability of different systems and software applications to communicate, exchange data, and use the information that has been exchanged. It plays a crucial role in ensuring seamless access to accurate and up-to-date patient information across various healthcare settings, leading to improved coordination of care and patient outcomes.
Challenges Associated with Data Exchange
- Standardization: Lack of standardized formats for data exchange makes it difficult for different systems to understand and interpret the information shared.
- Privacy and Security Concerns: Ensuring the secure exchange of sensitive patient data while maintaining patient privacy is a major challenge in interoperability.
- Technical Hurdles: Variations in data formats, protocols, and interfaces between systems can hinder smooth data exchange and interoperability.
- Cost and Resource Constraints: Implementing interoperable systems and overcoming technical barriers often require significant financial resources and expertise.
Strategies to Improve Interoperability
- Adoption of Health Information Exchange (HIE) platforms: HIE platforms facilitate the secure sharing of patient information across different healthcare organizations.
- Establishment of Data Standards: Developing and adhering to data standards such as HL7 and FHIR can enhance interoperability by ensuring data consistency and compatibility.
- Enhanced Data Governance: Implementing robust data governance policies and procedures can help address privacy, security, and quality issues related to data exchange.
- Promotion of Interoperable Systems: Encouraging the use of interoperable systems through incentives and regulations can drive organizations towards better data exchange practices.
Cybersecurity in Health Information Technology

Ensuring cybersecurity in health information technology is crucial to safeguarding sensitive patient data and maintaining the integrity of healthcare systems.
Healthcare organizations face a variety of cybersecurity threats that can compromise patient information and disrupt operations. Some common threats include:
Common Cybersecurity Threats in Healthcare
- Phishing attacks targeting employees to gain access to sensitive data.
- Ransomware attacks that encrypt data and demand payment for decryption.
- Malware infections that can spread through networks and compromise systems.
- Insider threats from employees or third parties with access to confidential information.
Implementing best practices can help enhance cybersecurity measures in healthcare settings and mitigate these threats. Some strategies include:
Best Practices for Enhancing Cybersecurity in Healthcare
- Regular employee training on cybersecurity awareness and protocols.
- Implementing access controls to restrict unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Encrypting data to protect information in transit and at rest.
- Conducting regular security audits and risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities.
- Implementing multi-factor authentication to enhance access security.
Telemedicine and Remote Patient Monitoring
Telemedicine and remote patient monitoring are revolutionizing the way healthcare is delivered, especially in today's digital age. These technologies have the potential to greatly improve patient care and outcomes by providing access to medical services and monitoring tools remotely.
Telemedicine: Transforming Healthcare Delivery
Telemedicine involves the use of technology to facilitate virtual healthcare visits, consultations, and monitoring. It allows patients to connect with healthcare providers from the comfort of their own homes, eliminating the need for in-person visits. This not only increases convenience for patients but also expands access to care for those in remote or underserved areas.
Telemedicine has the potential to reduce healthcare costs, improve patient satisfaction, and enhance overall healthcare outcomes.
Remote Patient Monitoring: Improving Patient Care
Remote patient monitoring enables healthcare providers to track patients' vital signs, symptoms, and other health data in real-time from a distance. By continuously monitoring patients outside of traditional clinical settings, healthcare professionals can detect and address health issues earlier, leading to better management of chronic conditions and preventing unnecessary hospitalizations.
This technology empowers patients to take a more active role in their own healthcare and promotes better communication between patients and providers.
Future Potential of Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring Technologies
The future of telemedicine and remote patient monitoring looks promising, with ongoing advancements in technology and increased acceptance of virtual care options. As these technologies continue to evolve, we can expect to see more personalized and efficient healthcare delivery models.
The integration of artificial intelligence and wearable devices in telemedicine and remote monitoring will further enhance the capabilities of these tools, allowing for more precise diagnostics and tailored treatment plans. Ultimately, telemedicine and remote patient monitoring have the potential to transform the healthcare landscape by making care more accessible, convenient, and effective for patients around the world.
Closure
In conclusion, the discussion on the future of health information technology highlights the importance of embracing advancements while addressing the challenges to ensure optimal patient care and outcomes.
User Queries
How important is interoperability in health information technology?
Interoperability is crucial as it allows different healthcare systems to seamlessly communicate and share data, leading to better coordination of care and improved patient outcomes.
What are some common cybersecurity threats faced by health information systems?
Common cybersecurity threats include ransomware attacks, data breaches, phishing attempts, and malware infections that can compromise the confidentiality and integrity of health data.
How is telemedicine transforming healthcare delivery?
Telemedicine enables healthcare professionals to provide remote consultations, diagnosis, and treatment to patients, improving access to care, especially in underserved areas.